Elastomeric connectors, often dubbed as rubber connectors or rubber interconnects, have emerged as indispensable passive components, providing flexible and reliable electrical connections. With roots tracing back to the mid to late 20th century, these connectors have continuously evolved to meet the demands of advancing electronics and the relentless march towards miniaturization. Let’s delve into the historical landscape where elastomeric connectors first made their mark:
Pioneering Applications:
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Interconnects. Initially, elastomeric connectors found their footing in establishing electrical connections between printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other electronic components. Their inherent flexibility and adaptability to accommodate misalignments rendered them optimal for connecting PCBs in devices grappling with space constraints or mechanical movements.
- Portable Electronics. As the era of portable and handheld electronic devices dawned, elastomeric connectors seamlessly integrated into gadgets like calculators, digital watches, and handheld electronic games. These connectors provided a compact yet reliable solution for establishing electrical connections among diverse components.
- Consumer Electronics. With the surge in consumer electronics, elastomeric connectors became ubiquitous in devices such as televisions, radios, audio equipment, and home appliances. Their versatility and cost-effectiveness made them the go-to choice for connecting internal components, including displays, control panels, and circuit boards.
- Medical Devices. In the medical realm, elastomeric connectors found their way into various medical devices and equipment, including diagnostic instruments and patient monitoring devices. Their ability to withstand sterilization processes and uphold electrical integrity positioned them as indispensable components in medical applications.
- Automotive Electronics. Elastomeric connectors made significant inroads into automotive electronics, facilitating electrical connections in dashboard displays, entertainment systems, engine control units, and other vehicular components. Their resilience to temperature variations, vibrations, and mechanical stresses made them indispensable in automotive environments.
Modern Applications of Wire-Based Elastomers
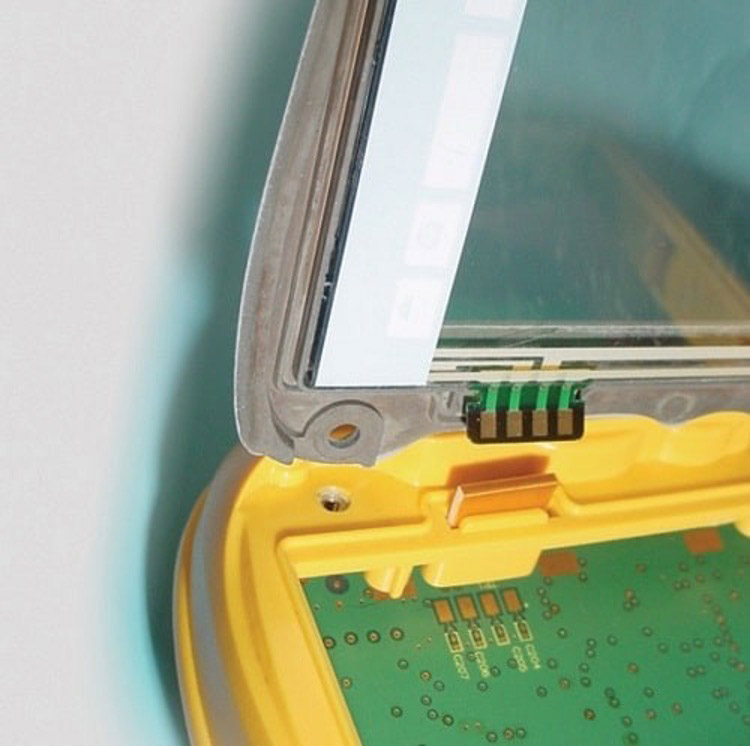

Wire-based elastomers, also referred to as wire-based elastomeric connectors or wire-based rubber connectors, serve diverse roles across different industries, owing to their unique properties and adaptability:
- Flexible Circuits and Interconnects. Wire-based elastomers play a pivotal role in flexible circuits and interconnects, offering a flexible yet reliable means of establishing electrical connections between components. They facilitate signal transmission and power distribution in applications where traditional rigid connectors prove impractical due to space constraints or mechanical movements.
- Medical Devices. Wire-based elastomers find extensive utilization in an array of medical devices and equipment, ranging from wearable health monitors to medical sensors and diagnostic instruments. Their flexibility and biocompatibility render them suitable for applications involving direct contact with the human body.
- Automotive Electronics. Within the automotive domain, wire-based elastomers are instrumental in various electronic systems and components. They enable electrical connections in dashboard displays, infotainment systems, navigation systems, and engine control units, offering resilience to the rigorous conditions prevalent in automotive environments.
- Consumer Electronics. Wire-based elastomers are ubiquitous in consumer electronics, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable devices. They facilitate connections among internal components like displays, touchscreens, batteries, and cameras, ensuring flexibility and reliability in devices characterized by compact designs and frequent mechanical movements.
- Industrial Applications. In industrial settings, wire-based elastomers find application in robotics, automation systems, and machinery, facilitating electrical connections in moving parts and components. They ensure reliable signal transmission and power distribution in dynamic environments.
- Aerospace and Defense. Wire-based elastomers play a pivotal role in aerospace and defense applications, featuring in electronic systems aboard aircraft, satellites, and military vehicles. They enable flexible and robust electrical connections capable of withstanding the extreme conditions prevalent in aerospace and defense environments.
How Our Elastomeric Connectors Work
- Contact Formation. Elastomeric connectors typically consist of alternating layers of conductive and non-conductive materials. Upon compression between two surfaces, such as two PCBs, the conductive layers within the connector establish contact with corresponding conductive pads or traces on the respective PCBs.
- Conductive Pathway. The compressive force applied to the elastomeric connector ensures a reliable electrical connection between the mating PCBs. This paves the way for a conductive pathway, facilitating the passage of power and\or electrical signals.
- Flexibility and Compliance. A key advantage of elastomeric connectors lies in their flexibility and compliance. This inherent characteristic enables them to conform to the surface irregularities of the PCB and accommodate slight misalignments or variations in the contact points, ensuring consistent and reliable electrical contact across the PCB’s entire surface.
- Low Contact Resistance. Engineered to feature low contact resistance, elastomeric connectors minimize signal loss. This attribute significantly contributes to the reliability and accuracy of projects which use elastomeric connectors.
The Dynamics of Force vs. Deflection
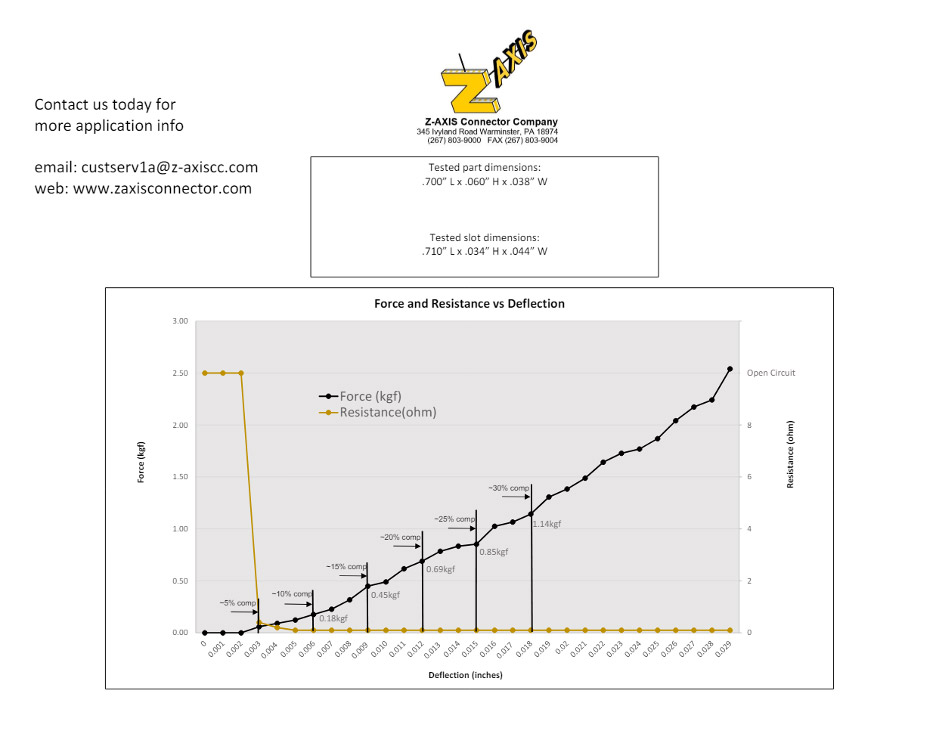
The force vs. deflection characteristics of elastomeric connectors exhibit variability contingent upon factors such as material composition, design parameters, and application requirements. Nevertheless, elastomeric connectors typically demonstrate a linear then non-linear force-deflection response, characterized by the following phases:
- Initial Compression. Elastomeric connectors necessitate minimal force during the initial compression phase to establish contact between the conductive layers. This phase is marked by low force and minimal deflection as the connector commences deformation under applied pressure.
- Linear Region. With increasing compression force, the elastomeric material undergoes elastic deformation, resulting in a linear escalation of force with deflection. This phase typically maintains consistent behavior.
- Plastic Deformation. Beyond a certain threshold, the elastomeric material may undergo plastic deformation, leading to permanent alterations in its molecular structure. This phase is characterized by a significant surge in force, potentially resulting in irreversible changes to the connector’s shape.
- Maximum Compression. Eventually, the force vs. deflection curve attains a plateau or maximum value, indicative of the elastomeric connector reaching full compression or mechanical limits. At this juncture, further increases in force may yield marginal additional deflection.
Advantages of Elastomeric Connectors
Elastomeric connectors offer a plethora of advantages, rendering them conducive to diverse applications across various industries:
- Flexibility. Elastomeric connectors exhibit unparalleled flexibility, effortlessly conforming to irregular surfaces and accommodating misalignments between mating components.
- Vibration and Shock Absorption. With inherent damping properties, elastomeric connectors excel in absorbing vibrations and shocks, ensuring electrical integrity and safeguarding sensitive components from damage.
- Low Contact Resistance. Elastomeric connectors boast low contact resistance, facilitating efficient electrical conductivity and minimizing signal loss, thereby ensuring optimal performance.
- Tolerance to Misalignment. The ability to tolerate slight misalignments between mating components simplifies assembly processes and enhances overall reliability by minimizing the risk of connector damage or failure.
- Cost-Effectiveness. Elastomeric connectors offer a cost-effective solution, particularly in scenarios necessitating a high volume of interconnections, owing to their simplified design and manufacturing processes.
- Durability and Longevity. Renowned for their durability, elastomeric connectors can withstand thousands of mating cycles without compromising performance, thereby reducing maintenance requirements and total cost of ownership.
- Versatility. Available in diverse shapes, sizes, and configurations, elastomeric connectors can be customized to meet specific design specifications, making them suitable for a myriad of applications across industries.
Conclusion
Elastomeric connectors epitomize a convergence of flexibility, conductivity, and reliability. Their multifaceted utility spans across industries, underpinning technological advancements and propelling innovation. At Z-Axis Connector Company, we remain steadfast in our commitment to harnessing the potential of elastomeric connectors to foster precision and reliability.
Feel free to reach out for further insights or explore our comprehensive range of solutions tailored to elevate your project and unlock new frontiers in electronic innovation.
Contact us today!
